Magnetism, that invisible force that attracts or repels, is more common than you might think. Where can magnetism be found? From the smallest atoms to the vast reaches of space, magnetism plays a vital role in our universe and everyday lives. Let’s explore the fascinating world of magnetism and uncover its presence in various forms.
Magnetism in Everyday Objects
Magnetism is all around us, hidden in plain sight within many everyday objects. Your refrigerator door relies on magnets to stay securely shut. Loudspeakers use magnets to convert electrical signals into sound waves. Credit cards contain magnetic stripes that store your personal information. Electric motors, found in everything from power tools to electric cars, harness the power of magnetism to generate motion. Even the simple act of using a compass relies on the Earth’s magnetic field to guide you.
 Examples of Magnetism in Everyday Life
Examples of Magnetism in Everyday Life
Natural Magnets: Lodestones and the Earth
Some materials exhibit magnetism naturally. Lodestones, a naturally occurring mineral magnetite, were the first magnets discovered by humans. These fascinating rocks possess a natural magnetic field, capable of attracting iron and other magnetic materials. Perhaps the largest and most significant natural magnet is Earth itself. Our planet generates a vast magnetic field that protects us from harmful solar radiation and allows for navigation using compasses. This geomagnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron within the Earth’s core.
 Lodestone and Earth's Magnetic Field
Lodestone and Earth's Magnetic Field
Electromagnetism: Harnessing Electricity and Magnetism
Where can magnetism be found in relation to electricity? The connection between electricity and magnetism, known as electromagnetism, is a fundamental force in physics. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and conversely, changing magnetic fields can induce electric currents. This principle is the foundation of numerous technologies, including generators, transformers, and inductors. Electromagnets, created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire wrapped around a core, are essential components in devices like MRI machines and industrial lifting cranes.
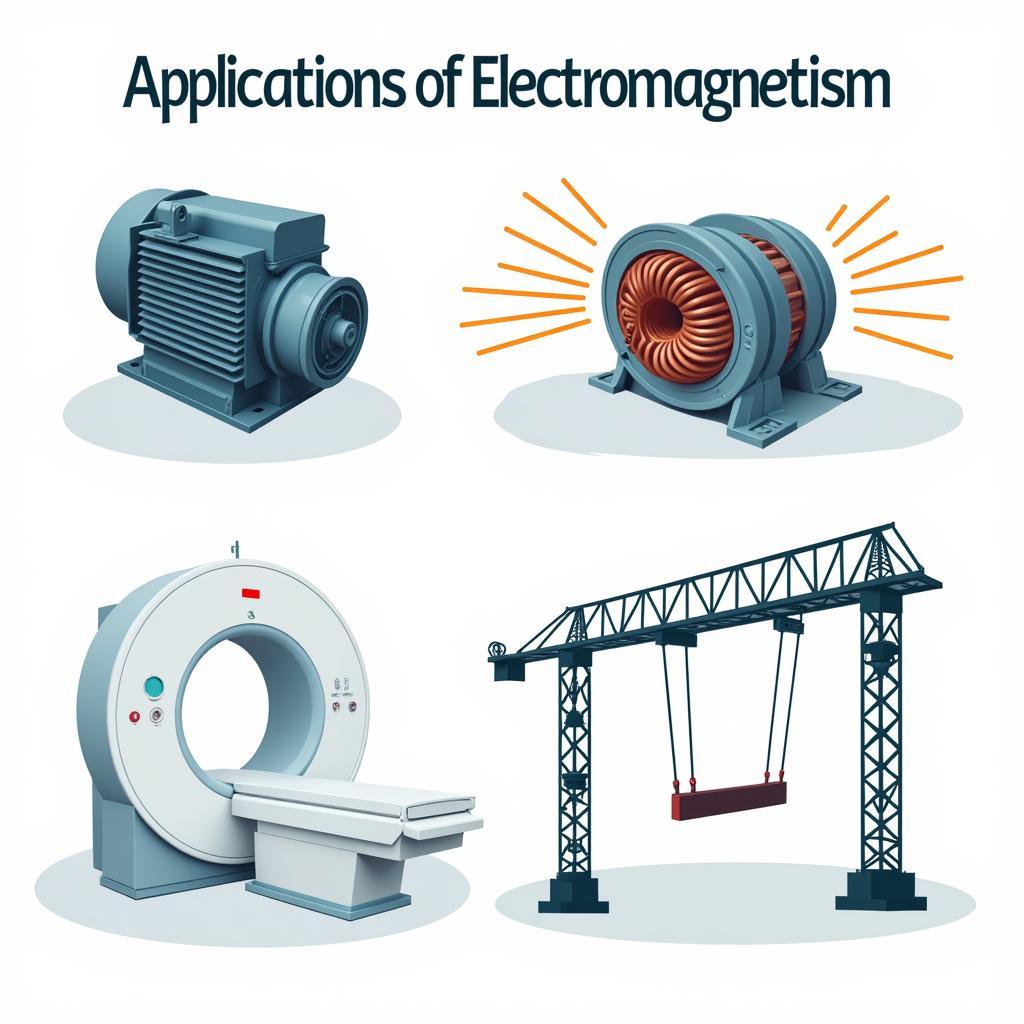 Applications of Electromagnetism
Applications of Electromagnetism
Magnetism at the Atomic Level
At the heart of all magnetism lies the movement of charged particles, primarily electrons. Electrons orbiting an atom’s nucleus generate tiny magnetic fields. In most materials, these fields are randomly oriented and cancel each other out, resulting in no overall magnetism. However, in ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt, the electron spins align, creating a strong magnetic field. This alignment is what gives these materials their magnetic properties. Understanding magnetism at the atomic level is crucial for developing new magnetic materials and technologies.
Where Can Magnetism Be Found in Space?
Magnetism isn’t confined to Earth; it’s a pervasive force throughout the universe. Stars, including our sun, possess powerful magnetic fields that influence their behavior. These magnetic fields can give rise to solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can impact Earth’s atmosphere and technology. Neutron stars, the incredibly dense remnants of massive stars, have the strongest magnetic fields in the universe, billions of times stronger than Earth’s. Even galaxies themselves possess magnetic fields that play a role in their structure and evolution.
Conclusion
So, where can magnetism be found? As we’ve explored, magnetism is a fundamental force present everywhere, from the smallest atoms to the vast expanse of space. Its influence shapes our world, powers our technologies, and plays a vital role in the universe’s workings. Understanding where magnetism exists and how it works is key to unlocking further advancements in science and technology. If you are planning a trip to Hanoi and want to explore the city and its surrounding areas related to magnetism and science, consider using TRAVELCAR’s 16-seater, 29-seater, or 45-seater vehicle rental services.
FAQ
- What is the strongest natural magnet? Lodestone.
- What is electromagnetism? The interaction of electric currents and magnetic fields.
- How does the Earth generate its magnetic field? Through the movement of molten iron in its core.
- What are some examples of magnetic materials? Iron, nickel, and cobalt.
- Where can I learn more about hoàng mai ở đâu?
- Why are magnetic fields important? They protect us from solar radiation and enable navigation.
- How does magnetism relate to technology? It’s crucial for devices like motors, generators, and MRI machines.
Situations and Questions
Situation: You’re trying to explain to a child how a compass works.
Question: Why does the compass needle always point north?
Situation: You’re curious about how electricity is generated.
Question: How do power plants use magnetism to create electricity?
Further Exploration
Explore related articles on our website about electric fields and the Earth’s core.
Call to Action
For transportation needs in Hanoi, contact TRAVELCAR at 0372960696, TRAVELCAR[email protected], or visit us at 260 Cầu Giấy, Hanoi. We have a 24/7 customer service team.