Have you ever wondered how messages zip around your body faster than a jet setting off on a round-the-world adventure? It’s like a high-speed train network, but instead of tracks, we have nerves, and the passengers are electrical signals called nerve impulses. A common question that pops up is, “Can these impulses travel in both directions?” It’s a fascinating thought, isn’t it? Imagine visiting the Eiffel Tower and sending a postcard back home through the same route! While our nervous system is amazing, it’s not quite like that. Let’s dive into the world of neurons and uncover the truth behind this intriguing question.
One-Way Streets: The Flow of Nerve Impulses
Picture this: you’re strolling down Lombard Street in San Francisco, famous for its winding, one-way road. Similarly, nerve impulses also travel in one direction, but instead of twists and turns, their path is determined by the neuron’s structure.
How Nerve Impulses Travel: A Journey in One Direction
Neurons, the building blocks of our nervous system, are like tiny messengers with specialized structures:
- Dendrites: The “receivers,” like antennas picking up signals from other neurons.
- Cell Body: The control center, processing incoming signals.
- Axon: The long, cable-like fiber transmitting the signal.
- Synapse: The junction where the axon of one neuron connects with the dendrite of another.
The journey begins when a stimulus, let’s say the breathtaking view from the Golden Gate Bridge, triggers an electrical signal in the dendrites. This signal then travels through the cell body and down the axon, like a wave of excitement rushing towards its destination.
The Role of Synapses: Ensuring One-Way Communication
At the synapse, the electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal. Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers, are released into the synaptic cleft, a tiny gap between neurons. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the receiving neuron’s dendrites, triggering a new electrical signal to continue the message.
Think of it as a relay race: the first runner (the electrical signal) passes the baton (neurotransmitter) to the next runner (the next neuron) at the exchange zone (synapse). This ensures that the message travels in one direction.
Why Not Both Ways? The Importance of Unidirectional Flow
Imagine the chaos if cars on Lombard Street could suddenly switch directions! Our nervous system relies on order and precision. The unidirectional flow of nerve impulses is crucial for:
- Coordinated Movement: From the intricate dance of a ballerina to a simple act like picking up a seashell, precise muscle control relies on the organized transmission of nerve impulses.
- Sensory Perception: The feeling of warm sand between your toes or the sweet scent of saltwater taffy is possible because sensory information travels in a specific direction – from sensory receptors to the brain.
- Clear Communication: Just like a phone call, neural communication requires a clear line between the sender and the receiver. Unidirectional flow prevents signals from getting mixed up and ensures accurate information processing.
FAQs: Unraveling More Mysteries of Nerve Impulses
Q: But what about reflexes? Don’t they involve two-way communication?
A: Reflexes are like shortcuts in the nervous system. They involve a simpler pathway, but the principle of one-way transmission still applies. Sensory neurons send signals to the spinal cord, where they connect with motor neurons that send signals back to the muscles, triggering a rapid response.
Q: Can the direction of nerve impulses be reversed in any situation?
A: In normal circumstances, no. However, in experimental settings and under specific conditions, researchers have been able to manipulate neurons to transmit signals in the reverse direction. This research helps us understand neuronal function in more detail.
Exploring the Wonders of Neural Communication and Travel
Understanding how nerve impulses travel is like unlocking a secret code that governs our every thought, feeling, and action. It’s a testament to the incredible complexity and efficiency of our bodies.
Just like a well-planned itinerary enhances your travel experience, the organized flow of information in our nervous system allows us to navigate the world around us, experience its wonders, and create lasting memories.
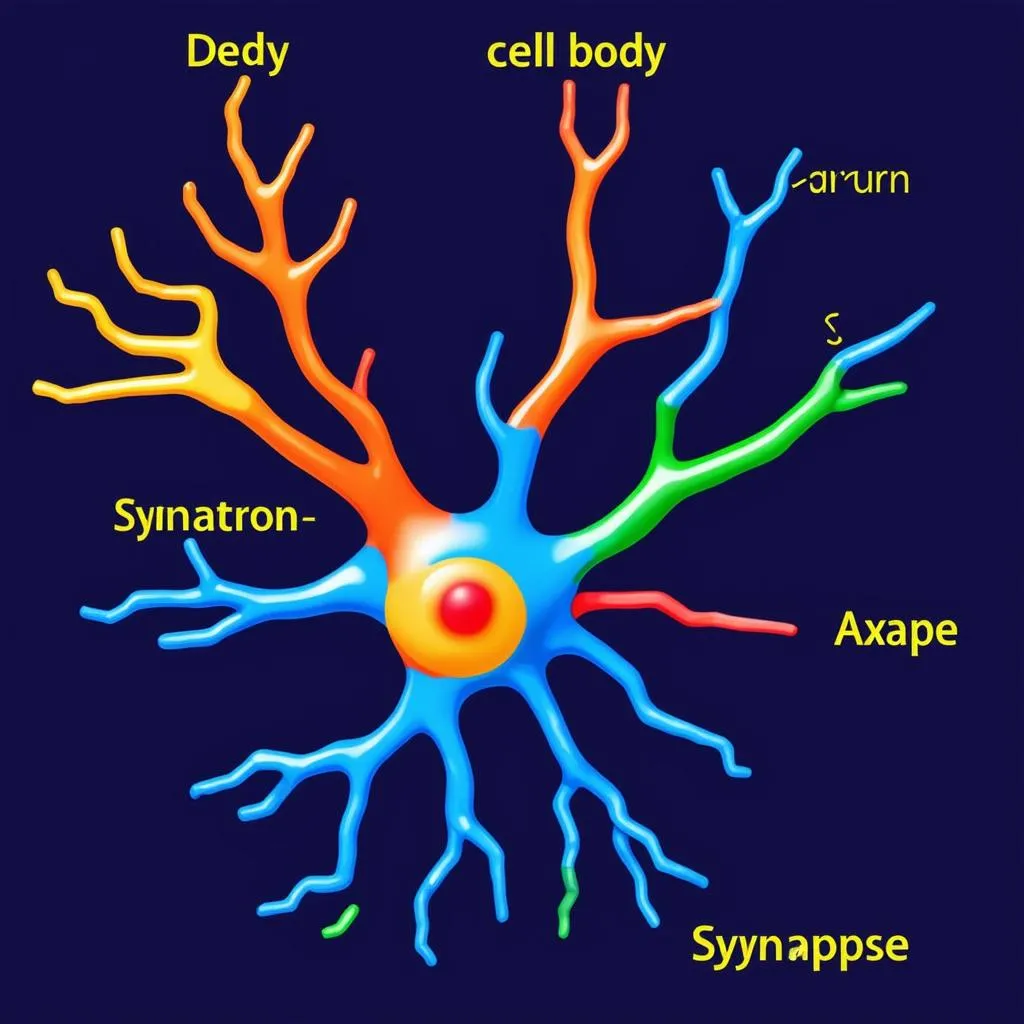 Structure of a Neuron
Structure of a Neuron
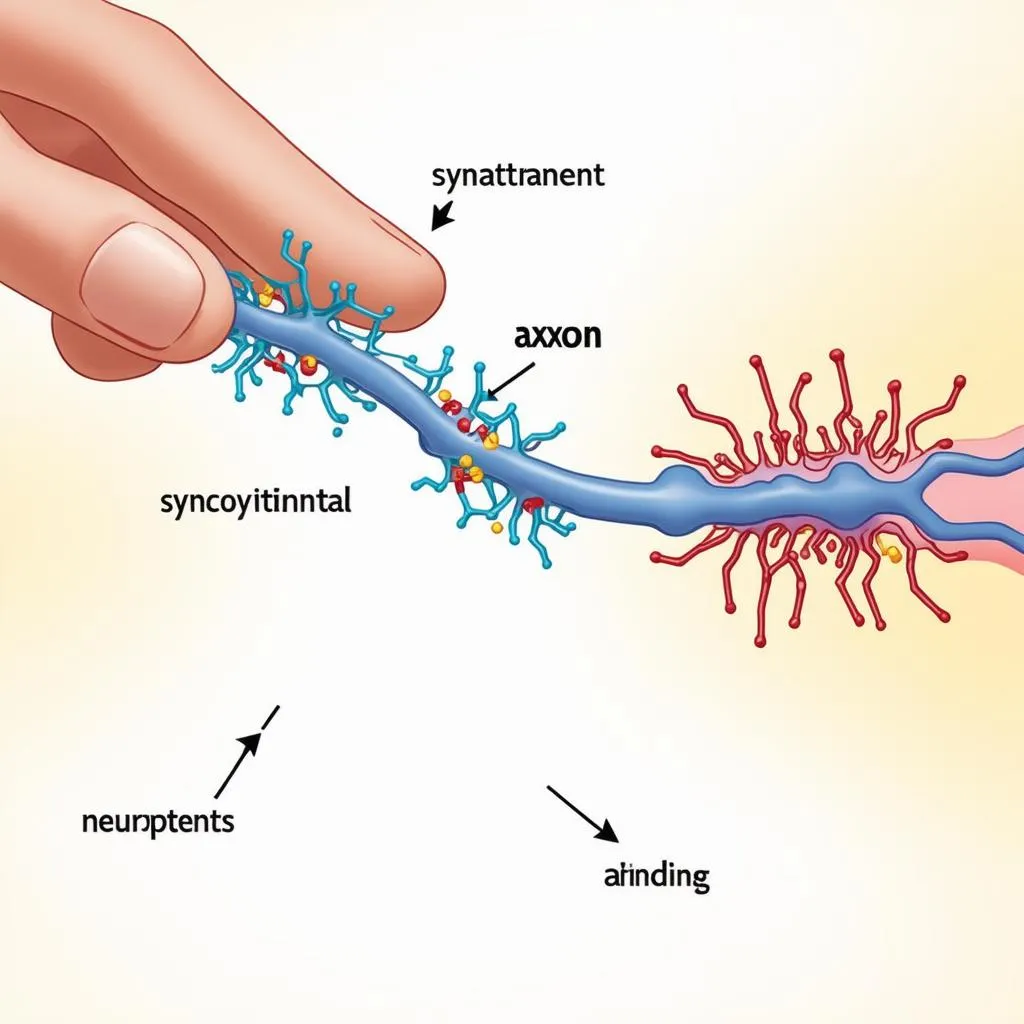 Synaptic Transmission
Synaptic Transmission
So, the next time you embark on a journey, take a moment to appreciate the incredible journey happening within you – the constant flow of nerve impulses, carrying messages at lightning speed, allowing you to experience the world in all its glory.