Have you ever wondered how your brain communicates with the rest of your body in a fraction of a second? Imagine visiting the bustling Times Square in New York City, and within a blink of an eye, you receive a message from a friend miles away in Central Park. That’s the speed and efficiency of our nervous system, transmitting information through nerve impulses. But how exactly does a nerve signal travel? Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the fascinating order of events in this intricate biological process.
Understanding the Basics: Neurons and Nerve Impulses
Before we delve into the sequence, let’s familiarize ourselves with the key players: neurons. Neurons are the specialized cells of the nervous system responsible for transmitting information. Picture them as messengers carrying coded messages throughout your body. These messages, known as nerve impulses or action potentials, are electrical signals that travel along the neuron’s membrane.
A Nerve Signal’s Journey: Following the Path
The journey of a nerve signal follows a specific order, much like a well-coordinated relay race:
1. Resting Potential: The Calm Before the Storm
In its resting state, a neuron maintains a difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of its cell membrane. This difference, called the resting potential, is like a coiled spring ready to be released.
2. Stimulus: The Trigger
A stimulus, such as a touch, sound, or even a thought, triggers the nerve impulse. Imagine standing near the Trevi Fountain in Rome and suddenly feeling a splash of water. That sensation acts as a stimulus, initiating a nerve impulse.
3. Depolarization: The Domino Effect
The stimulus causes a change in the neuron’s membrane permeability, allowing positively charged sodium ions (Na+) to rush into the cell. This influx of positive charges disrupts the resting potential, causing a wave of depolarization to travel along the neuron’s axon. Think of it as a line of dominoes toppling over, one after another.
4. Repolarization: Restoring the Balance
After depolarization, the neuron needs to reset itself. This phase, known as repolarization, involves the outflow of positively charged potassium ions (K+) from the cell, restoring the negative charge inside.
5. Refractory Period: A Moment of Rest
After sending a signal, the neuron enters a brief refractory period during which it cannot immediately fire another impulse. This period ensures that the signal travels in one direction only, like a one-way street.
6. Synaptic Transmission: Passing the Baton
Once the nerve impulse reaches the end of the neuron’s axon, it encounters a synapse, a tiny gap between neurons. Here, the electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal. Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers, are released into the synapse and bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, initiating a new nerve impulse. This process is similar to passing a baton in a relay race, ensuring the message continues its journey.
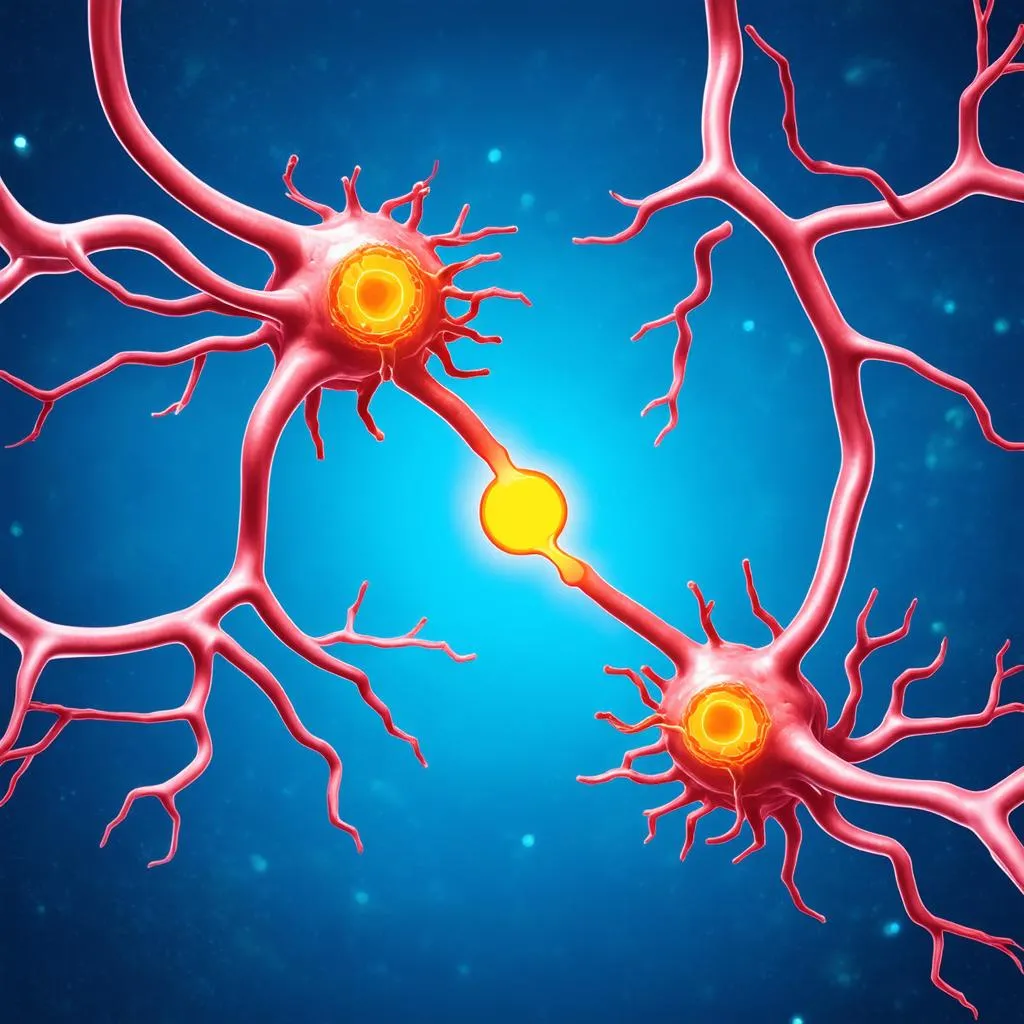 Neuron Synapse
Neuron Synapse
The Importance of Order: Maintaining Harmony
The specific order of events in nerve impulse transmission is crucial for the proper functioning of our nervous system. Any disruption in this sequence can lead to neurological disorders.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Nerve Impulses
Q: How fast do nerve impulses travel?
A: Nerve impulses can travel at speeds ranging from 1 to 120 meters per second, depending on the type of neuron and the presence of myelin, a fatty substance that insulates the axon.
Q: What factors can affect nerve impulse conduction?
A: Factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of drugs or toxins can influence the speed and efficiency of nerve impulse transmission.
Q: Can nerve impulses travel in both directions?
A: Nerve impulses typically travel in one direction only, from the dendrites (receiving end) to the axon terminal (transmitting end) of a neuron. However, in some cases, such as in sensory neurons, the impulse can travel towards the cell body.
Travelcar.edu.vn: Your Guide to Exploring the World
Just as nerve impulses efficiently relay information throughout the body, travelcar.edu.vn aims to provide you with seamless travel experiences. Whether you’re seeking adventure in the vibrant streets of Tokyo or relaxation on the pristine beaches of Bali, we’ve got you covered.
 Travel Destinations
Travel Destinations
Conclusion: Appreciating the Marvel of Nerve Impulses
The next time you react to a stimulus, take a moment to appreciate the intricate and rapid-fire communication happening within your nervous system. The precise order of events in nerve impulse transmission highlights the remarkable complexity and efficiency of our biological design.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and travel experiences in the comments below. Let’s continue to explore the wonders of the world, both internal and external!