Have you ever wondered how you can react so quickly to a sudden event? Like catching a falling object or swiftly moving your hand away from a hot stove? This remarkable ability is all thanks to the lightning-fast communication network within our bodies – the nervous system! And at the heart of this intricate system lies the nerve signal, a tiny electrical impulse that carries vital information throughout our body.
The Journey of a Nerve Signal: A Whirlwind Tour
Think of a nerve signal like a traveler embarking on an exciting journey. The starting point? A sensory receptor, such as the touch receptors on your skin or the photoreceptors in your eyes. When stimulated, these receptors generate a nerve signal, our tiny traveler.
But where does the signal go next?
1. Down the Neuron Highway: The Axon
The signal first embarks on a journey down the axon, a long, slender fiber that acts like a highway within the neuron. Imagine this as a scenic route through the countryside, with the signal speeding along the axon like a car on a highway.
2. Jumping the Gap: The Synapse
The journey isn’t a straight shot though! Eventually, the signal reaches a junction called the synapse. This is where things get really interesting! The synapse is a tiny gap between two neurons, and our signal needs a way to cross it.
Imagine the synapse as a river our traveler encounters along the way. To cross, the signal transforms into a chemical messenger, a neurotransmitter, and hops onto a tiny raft (vesicle) to ferry across the river (synapse) to the next neuron.
3. Continuing the Journey: Next Neuron
Once safely across the synapse, the neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the next neuron, generating a new nerve signal. The journey continues, with the signal traveling through multiple neurons, like a relay race, until it reaches its final destination.
4. Reaching the Destination: Brain or Effector
The final destination could be the brain, where the signal is processed and interpreted, allowing us to perceive sensations, make decisions, and form memories. Alternatively, the signal might travel to an effector, like a muscle or gland, triggering a specific action, such as moving your hand or releasing hormones.
 Nervous System
Nervous System
The Importance of Understanding Nerve Signals
Understanding how nerve signals travel is crucial for comprehending how our body functions, from basic reflexes to complex thoughts and emotions. It also helps us grasp the mechanisms behind various neurological disorders and how treatments target specific points in the nervous system to alleviate symptoms.
FAQs about Nerve Signals
1. How fast do nerve signals travel?
Nerve signals can travel incredibly fast, ranging from 1 to 120 meters per second. This speed is crucial for quick reflexes and rapid information processing.
2. What factors can affect nerve signal transmission?
Factors like stress, fatigue, certain medications, and medical conditions like multiple sclerosis can affect the speed and efficiency of nerve signal transmission.
3. Can we improve the speed of nerve signals?
While we can’t magically increase the speed of nerve signals, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can support optimal nervous system function.
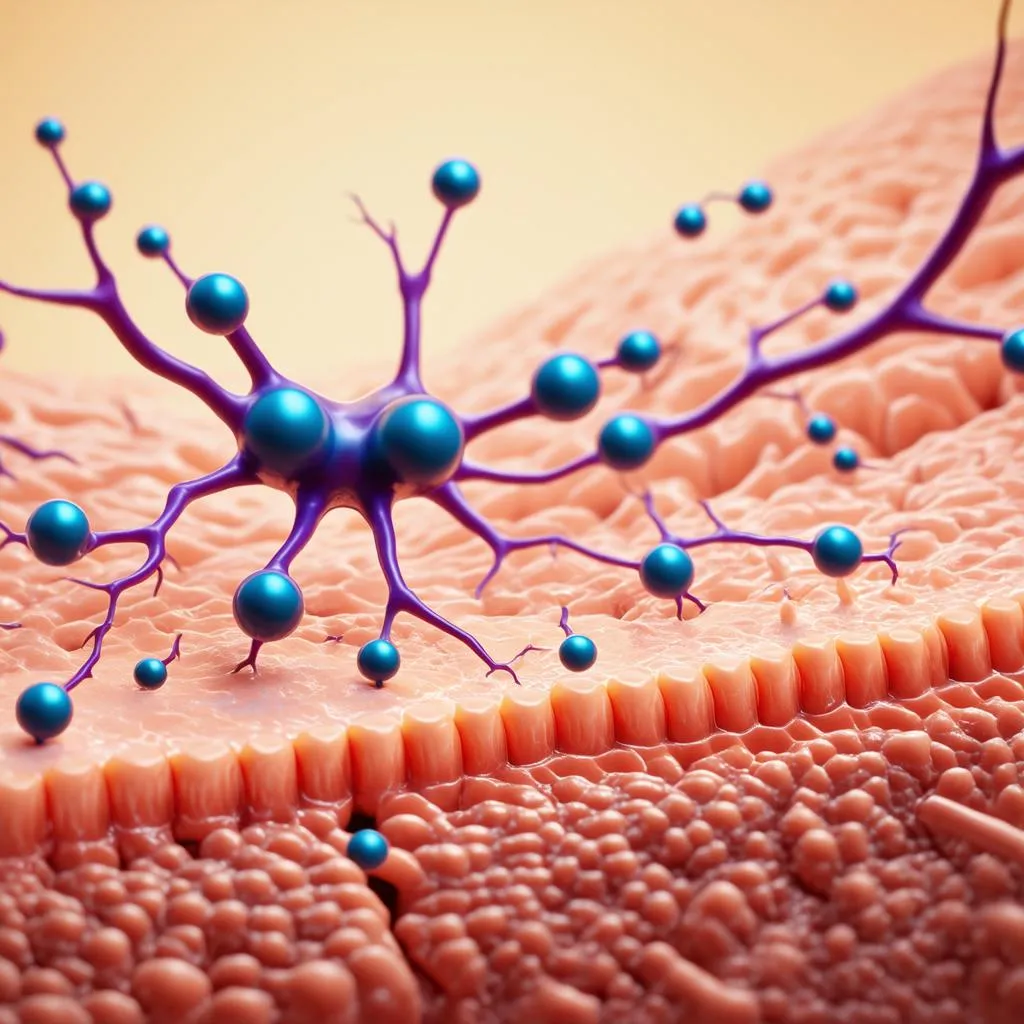 Neuron and Synapse
Neuron and Synapse
Travelcar.edu.vn: Your Guide to Exploring the World and Your Inner Universe
Just as a nerve signal navigates the complex pathways within our bodies, let travelcar.edu.vn be your guide to exploring the vast and fascinating world around us. From the bustling streets of Hanoi to the serene beaches of Phu Quoc, we provide insightful travel tips, destination guides, and inspiration to help you plan your next adventure.
Remember, every journey, whether internal or external, has the potential to be a transformative experience. So, pack your bags, open your mind, and embark on a journey of discovery with travelcar.edu.vn!