Have you ever wondered how your brain communicates with the rest of your body in a fraction of a second? It’s like a super-fast traveler zipping across a network of highways, except this traveler is a neuron, and its journey is called a nerve impulse. Buckle up, because we’re about to embark on an exciting adventure exploring the fascinating world of “A Neuron Travels.”
Understanding the Neuron’s Itinerary
Imagine a neuron as a traveler with a very important message to deliver. This message, the nerve impulse, is an electrochemical signal that travels from one part of the body to another. But how does it navigate this complex journey?
The Neuron’s Travel Route:
- Dendrites: The Starting Point: Our neuron traveler begins its journey at the dendrites, the neuron’s “receiving” end. They’re like bustling airports, constantly receiving signals from other neurons.
- Soma (Cell Body): Processing the Ticket: The signal then moves to the soma, the neuron’s main body. Think of this as the traveler checking its itinerary and preparing for the long journey ahead.
- Axon: The Highway: Next, the signal zooms down the axon, a long, cable-like extension of the neuron. This is the main highway of our journey, and it can be quite long – some axons stretch for meters!
- Myelin Sheath: The Fast Lane: In many neurons, the axon is covered in a fatty substance called the myelin sheath. This acts like a supercharger, allowing the signal to travel faster. Think of it as the express lane on our highway.
- Nodes of Ranvier: The Rest Stops: Along the axon, there are gaps in the myelin sheath called Nodes of Ranvier. These are like rest stops where the signal is boosted before continuing its journey.
- Axon Terminals: Reaching the Destination: Finally, the signal reaches the axon terminals, the neuron’s “sending” end. Here, it transmits the message to other neurons, muscles, or glands, completing its remarkable journey.
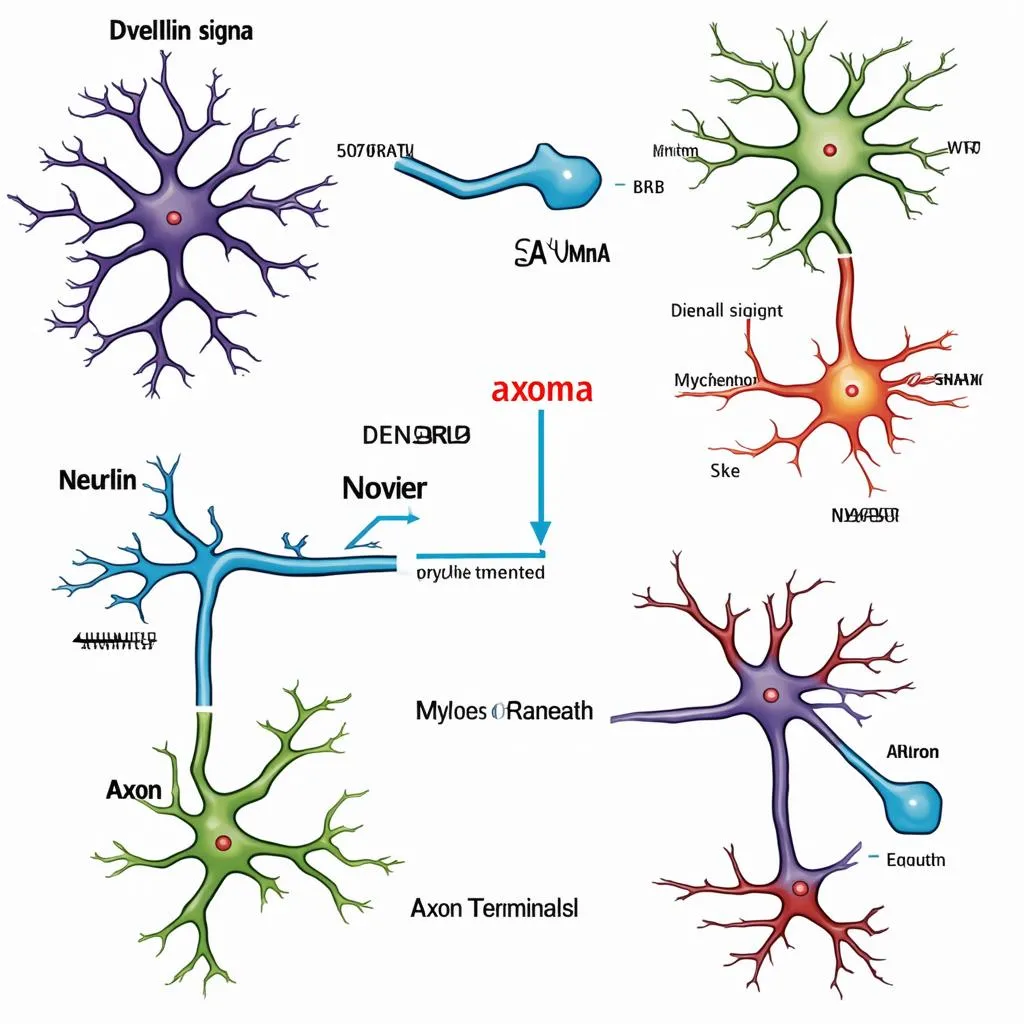 Neuron Travels: A Detailed Diagram
Neuron Travels: A Detailed Diagram
Why is the Neuron’s Journey Important?
This incredible journey of “a neuron travels” is essential for almost everything we do!
- Senses: When you smell freshly baked bread in a Parisian bakery or feel the warm sand of a Balinese beach between your toes, it’s because neurons are diligently transmitting sensory information to your brain.
- Movement: Every step you take, every word you speak, every move you make is orchestrated by neurons sending signals from your brain to your muscles.
- Thoughts and Emotions: Even your innermost thoughts and feelings are the result of intricate neural pathways firing away.
Frequently Asked Questions About “A Neuron Travels”
- How fast does a neuron travel? The speed of a nerve impulse can vary depending on factors like the presence of myelin, but it can be as fast as 270 miles per hour! That’s faster than a Formula 1 race car!
- Can anything go wrong during a neuron’s journey? Yes, diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) can damage the myelin sheath, disrupting the smooth flow of nerve impulses.
Planning Your Own “Travels” with Travelcar.edu.vn
Just like a neuron meticulously plans its route, planning is essential for a smooth and enjoyable travel experience. That’s where Travelcar.edu.vn comes in. We’re your trusted guide for all things travel, offering insightful tips, destination guides, and resources to help you plan your next adventure.
 Planning Your Next Trip with Travelcar.edu.vn
Planning Your Next Trip with Travelcar.edu.vn
Conclusion
The journey of “a neuron travels” is a testament to the wonders of our bodies. It’s a complex, fascinating process that underlies our every thought, feeling, and action. So, the next time you experience something amazing, take a moment to appreciate the incredible journey those tiny neurons are taking within you.
Have you ever experienced a moment where you were amazed by the speed of your body’s reactions? Share your story in the comments below! And be sure to explore more travel tips and inspiration on TRAVELCAR.edu.vn.
