Have you ever wondered how your brain tells your hand to wave hello to a fellow traveler? Or how you feel the warmth of the sun on your skin? It all comes down to the incredible journey of a signal through a neuron, the building block of your nervous system. Just like exploring a new city with its intricate network of roads, we’re about to embark on a journey through the information highway of your body.
The Neuron: Your Body’s Personal Courier Service
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit information throughout your body using electrical and chemical signals. Imagine a network of couriers delivering important messages – that’s essentially what neurons do. They are responsible for everything from feeling a gentle breeze on your face to solving complex mathematical equations.
The Journey Begins: Dendrites Receive the Signal
Our journey starts at the dendrites, the branch-like extensions of a neuron. Think of them as the “receiving docks” of our courier service. These dendrites pick up signals from other neurons or sensory receptors in your body.
The Axon: The Information Superhighway
Once the signal is received, it’s time to hit the road! The signal, now in the form of an electrical impulse, travels down the axon, a long, slender fiber that acts as the “information superhighway.” Just like a highway speeds up travel between cities, the axon ensures quick transmission of the signal.
Myelin Sheath: The Fast Lane
Some axons are covered in a fatty substance called the myelin sheath. This sheath acts like the “fast lane” on our highway, allowing the signal to travel faster and more efficiently.
Synapse: The Courier Exchange
Our signal has almost reached its destination! The axon terminal, located at the end of the axon, forms a junction with another neuron, muscle, or gland. This junction is called the synapse. Here, our courier hands off the message, but instead of a physical package, it’s a chemical signal called a neurotransmitter.
The Journey Continues
The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds to receptors on the receiving cell, triggering a response. And just like that, the message has been delivered! This process, from dendrite to synapse, repeats itself countless times, creating a complex and intricate communication network throughout your body.
Travel Planning for the Nervous System: Keeping Your Neurons Happy
Just like planning a trip, keeping your neurons in tip-top shape is crucial for a smooth and enjoyable journey!
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Provide your neurons with the fuel they need to function correctly. Think of it as packing nutritious snacks for your travels.
- Get Enough Sleep: Rest is essential for your nervous system to repair and recharge. Consider it a well-deserved layover on your journey.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can improve blood flow to the brain and promote the growth of new neurons. Imagine it as taking a scenic hike to keep your mind sharp.
FAQs about Neuron Signal Transmission
Q: How fast does a signal travel through a neuron?
A: The speed can vary depending on the type of neuron and the presence of myelin, but signals can travel as fast as 268 miles per hour!
Q: What happens if the signal transmission is disrupted?
A: Disruptions in signal transmission can lead to various neurological disorders, highlighting the importance of a healthy nervous system.
Q: Can we improve the speed of signal transmission?
A: While we can’t magically turn our neurons into Formula 1 race cars, a healthy lifestyle can certainly optimize their performance.
Travel Tip: Exploring the Wonders of the Human Body
Just as we explore new destinations, take some time to marvel at the incredible intricacies of your own body. From the complex network of neurons to the fascinating process of signal transmission, there’s a whole world of wonder waiting to be discovered!
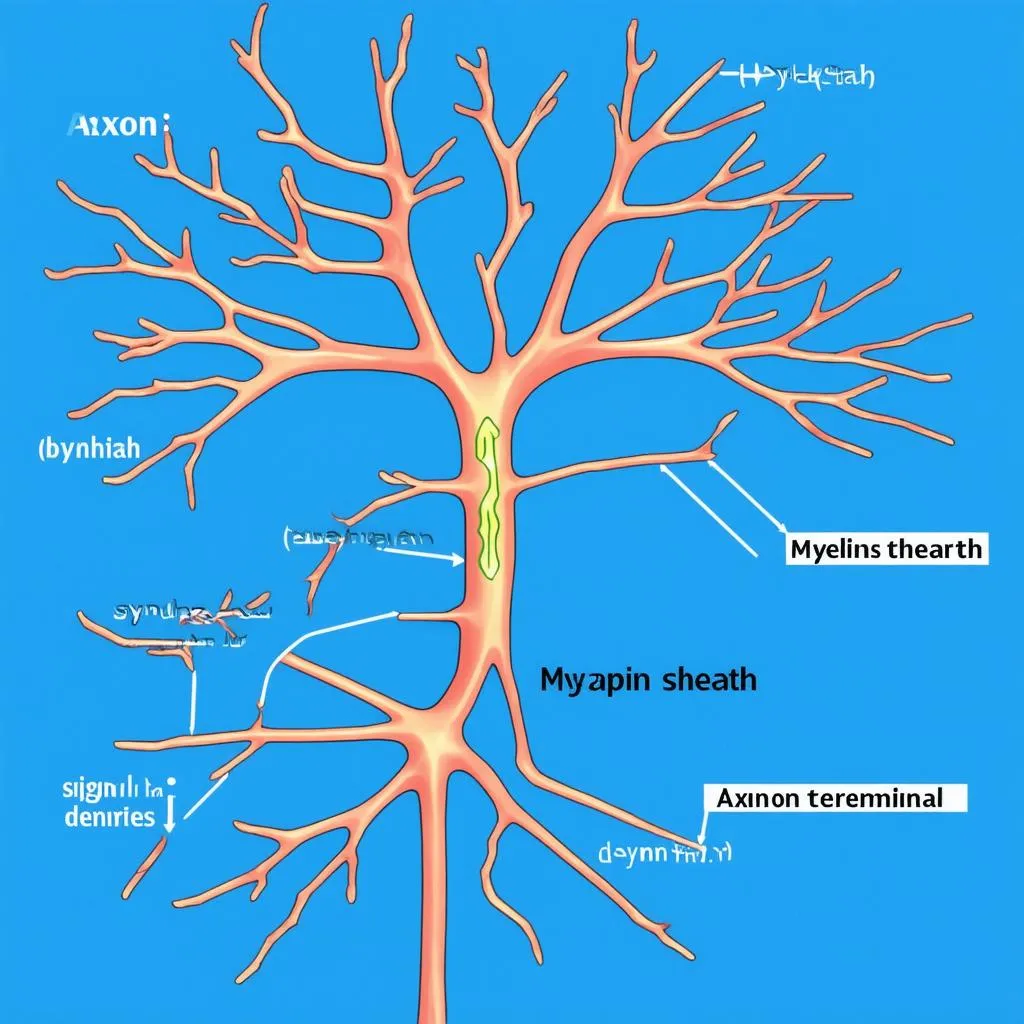 Neuron Signal Transmission
Neuron Signal Transmission
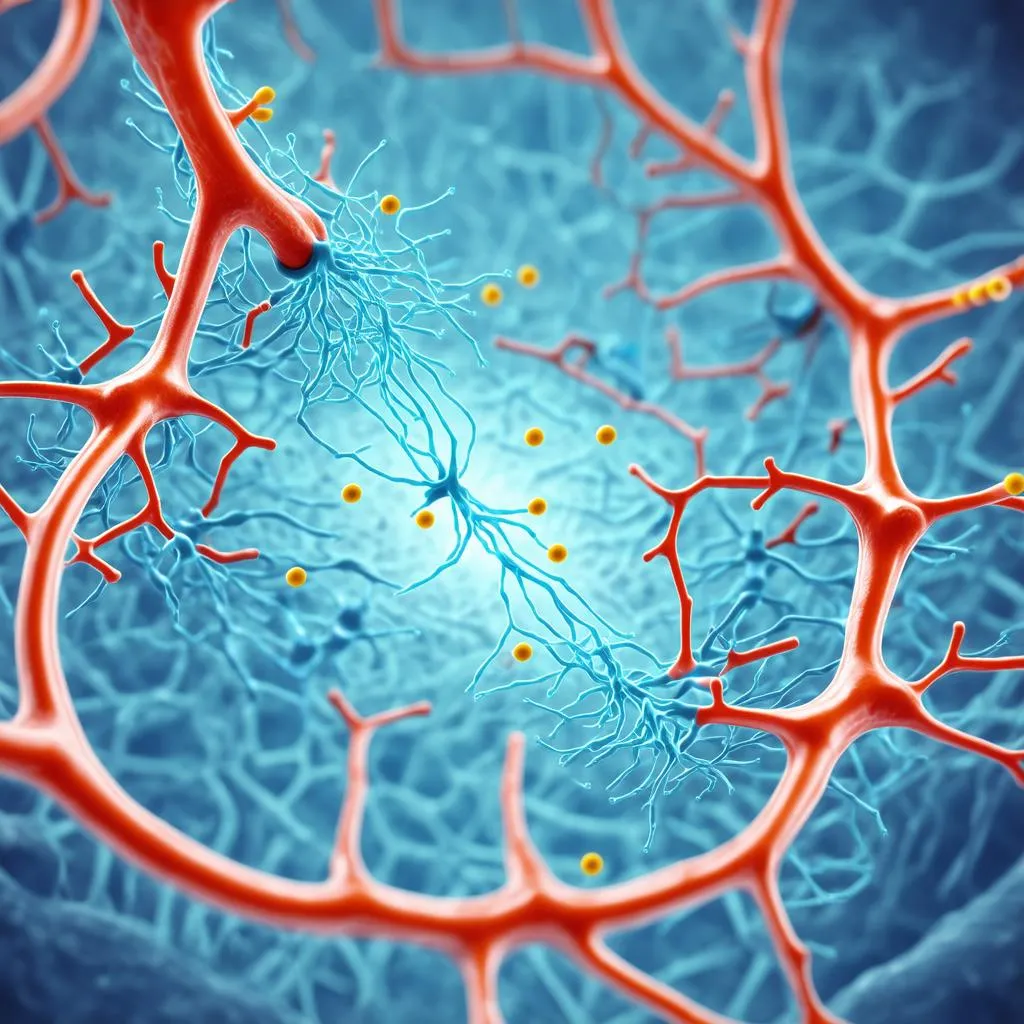 Synapse Close-Up
Synapse Close-Up
For more fascinating insights into the human body and travel tips, be sure to explore other informative articles on TRAVELCAR.edu.vn.