Imagine a serene lake in the heart of Hanoi, the sun glinting off the water. Suddenly, a pebble skips across the surface, sending ripples outwards in perfect circles. This, my friends, is a simple visualization of a wave, a disturbance that travels through a medium, transferring energy as it goes. Now, imagine that lake shrunk down to a single string, and you’ve got yourself a “travelling wave on a string”! This fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of waves and oscillations, has captivated scientists and students alike. Today, we’ll dive deep into this phenomenon, exploring its definition, characteristics, and real-world applications. Buckle up, it’s going to be a fascinating ride!
What Exactly is a Travelling Wave on a String?
In the simplest terms, a travelling wave on a string is a disturbance that propagates along a taut string, causing each point on the string to oscillate about its equilibrium position. Picture a string tied at one end to a door handle and held taut by your hand. As you flick your wrist up and down, you create a wave that travels along the string towards the door. This wave carries energy from your hand to the door, without any actual particles of the string moving in that direction. Fascinating, right?
Dissecting the Wave
Let’s break down the key characteristics of a travelling wave on a string:
- Amplitude: Think of this as the wave’s “height.” A larger amplitude means a more energetic wave, just like a bigger ripple on our lake.
- Wavelength: This is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave. Imagine measuring the distance between two peaks of the wave on our string.
- Frequency: This refers to how many complete waves pass a given point per second. Imagine counting how many ripples pass by a specific point on the lake each second.
- Wave Speed: This is the speed at which the wave propagates along the string. It depends on the tension of the string and its mass per unit length. A tighter string means a faster wave!
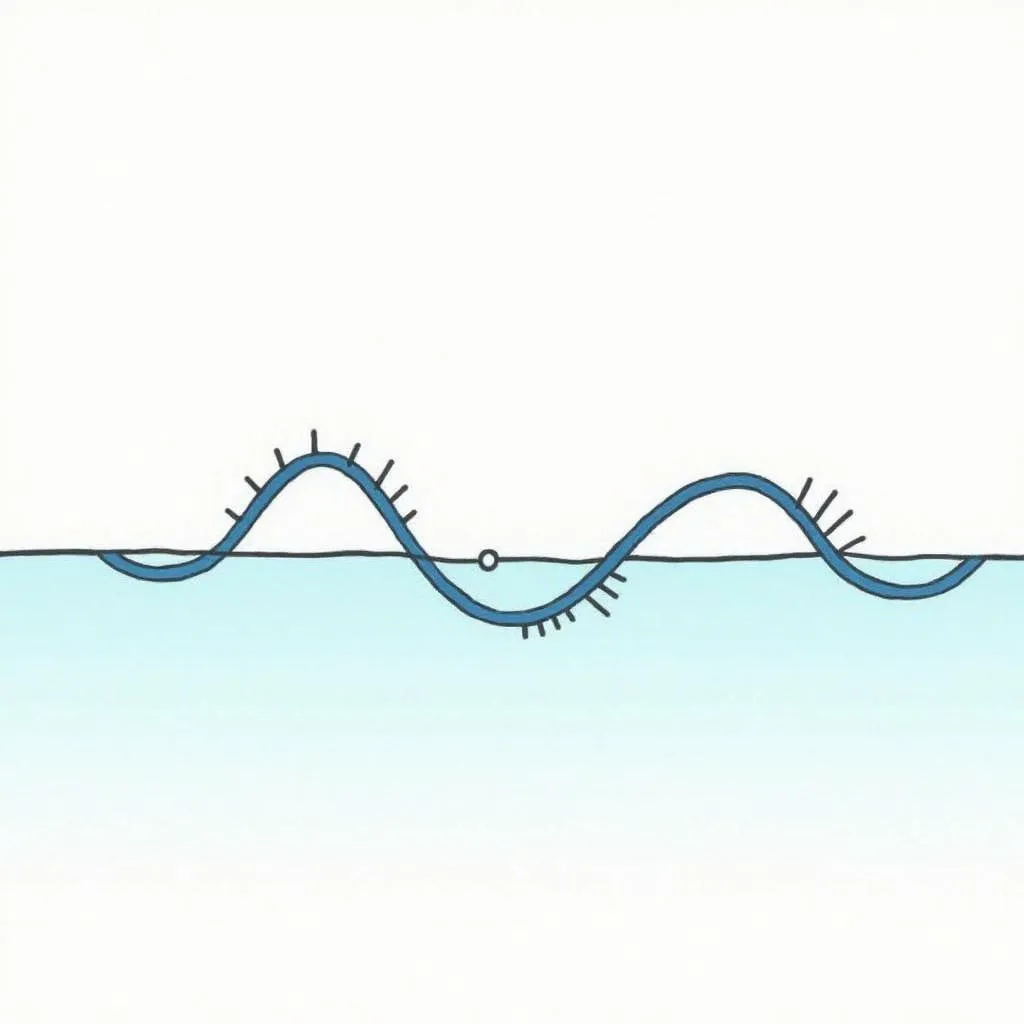 Illustration of a travelling wave on a string
Illustration of a travelling wave on a string
Delving Deeper: Understanding the Math and Physics
Now, for those who crave a bit more rigor, let’s add a dash of mathematical flavor. The equation that describes a travelling wave on a string is:
y(x,t) = A sin(kx – ωt + φ)
Don’t let the symbols scare you! This equation simply tells us how much each point on the string (represented by ‘y’) is displaced from its equilibrium position at a given time (‘t’) and position (‘x’). Here, ‘A’ is the amplitude, ‘k’ is the wave number (related to wavelength), ‘ω’ is the angular frequency (related to frequency), and ‘φ’ is the phase constant. This equation allows physicists to predict the exact shape and motion of the wave at any given moment.
Real-world Applications: Beyond the String
While the concept of a travelling wave on a string might seem abstract, its applications are surprisingly widespread. From musical instruments like guitars and violins, where the vibration of strings produces sound waves, to the transmission of information through fiber optic cables using light waves, understanding this fundamental phenomenon unlocks a world of possibilities.
The Human Connection
Interestingly, even in Vietnamese culture, the concept of waves resonates deeply. The rhythmic ebb and flow of life, the interconnectedness of all things, and the cyclical nature of time are all reflected in traditional Vietnamese beliefs and practices. Just like a wave on a string, our lives are a series of oscillations, with highs and lows, expansions and contractions.
 A Hanoi street musician serenading passersby with his guitar
A Hanoi street musician serenading passersby with his guitar
Have More Questions About Travelling Waves?
We’ve only just scratched the surface of this fascinating topic! Here are a few other questions you might be pondering:
- What are the different types of waves that can travel on a string?
- How does the tension in the string affect the speed of the wave?
- Can waves on a string interfere with each other?
If you’re eager to explore these questions further, don’t hesitate to reach out! Our team at TRAVELCAR is always happy to share our knowledge and passion for physics, travel, and the beautiful city of Hanoi. You can reach us at +84 0372 960 696 or [email protected]. And hey, if you’re ever in Hanoi and need a comfortable ride to explore the city’s hidden gems, we’ve got you covered with our fleet of 16-seater, 29-seater, and 45-seater vehicles.
So, the next time you see a ripple in a pond, hear a guitar strum, or even feel the pulse in your wrist, remember the incredible physics of travelling waves at play! It’s a reminder that even in the smallest of things, there’s a universe of wonder waiting to be discovered.

