Have you ever wondered how the majestic trees lining the Avenue des Champs-Élysées in Paris get their water? Or how the vibrant flowers at the Keukenhof Gardens in Amsterdam stay so hydrated? The answer lies in a fascinating process called transpiration, where water embarks on a remarkable journey through the plant’s vascular system.
The Intricate Plumbing System of Plants
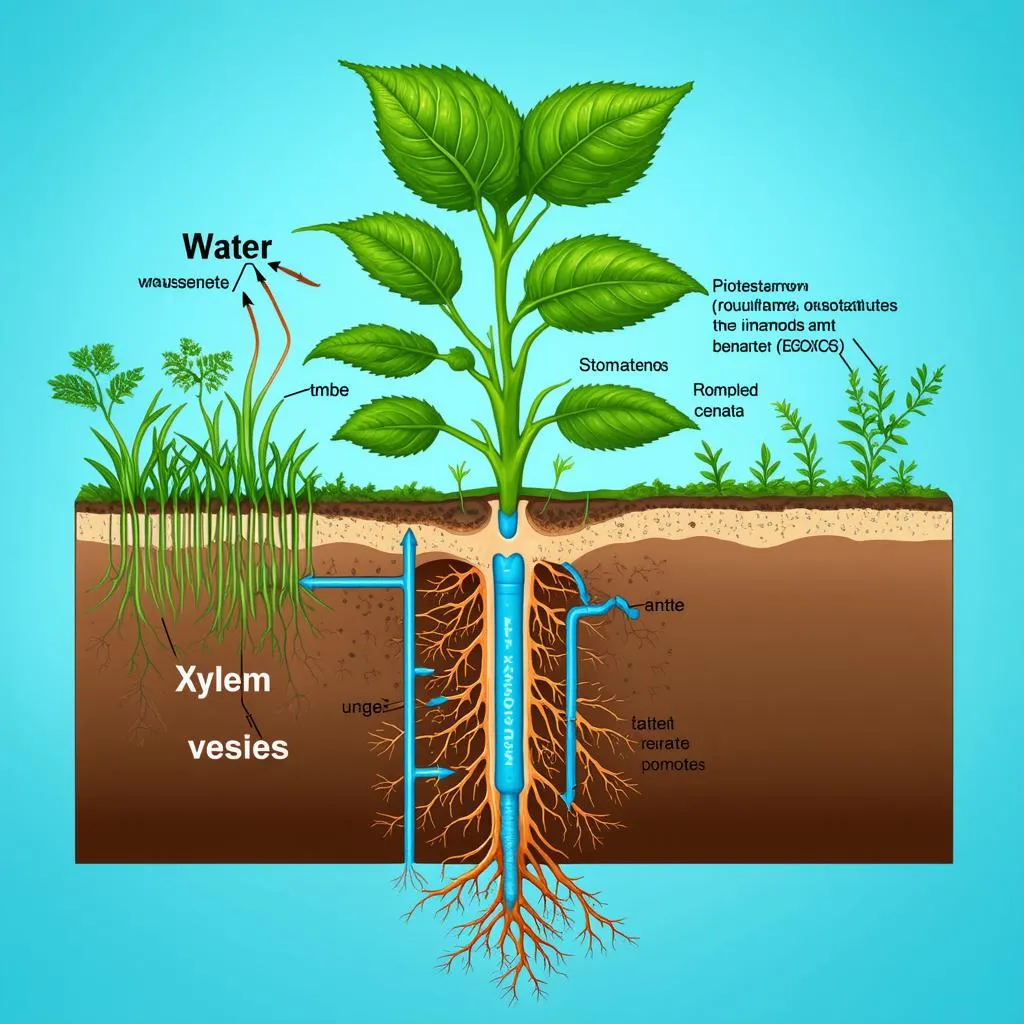
Plants, much like us, need water to survive. They’ve developed a specialized network of tissues that act like tiny pipes, transporting water and nutrients from the soil to every part of the plant. Let’s delve into the details of this intricate plumbing system.
Roots: The Thirsty Absorbers
Our journey begins underground, where the roots act as thirsty explorers, seeking out water in the soil. The root hairs, delicate extensions of the root system, provide a large surface area for absorption. This is similar to how the intricate canals of Venice maximize contact with water, ensuring efficient transportation.
Xylem: The Upward Journey
Once absorbed, water enters the xylem, a series of tube-like structures running vertically through the plant’s stem. Think of the xylem as a network of elevators, diligently carrying water upwards against gravity.
Transpiration: The Engine of the Journey
But what drives this upward movement? The answer lies in the leaves. As water evaporates from the tiny pores called stomata on the leaf surface, it creates a suction force. This force, known as transpiration pull, pulls water upwards through the xylem, much like a straw drawing up a refreshing drink.
The Importance of Cohesion and Adhesion
The journey of water through plants is also aided by the properties of water itself. Cohesion, the attraction between water molecules, helps them stick together, forming a continuous water column. Adhesion, the attraction between water molecules and the xylem walls, helps to pull the water column upwards.
 Water Transport System in Plants
Water Transport System in Plants
Factors Affecting Water Transport
Several factors can influence the efficiency of water transport in plants, much like how traffic conditions affect travel time. These include:
- Temperature: Just as warmer temperatures encourage us to drink more water, higher temperatures increase the rate of transpiration in plants.
- Humidity: High humidity can slow down transpiration, similar to how a humid day makes us feel less thirsty.
- Wind: Windy conditions can increase the rate of transpiration, much like how a breezy day dries our clothes faster.
- Light Intensity: Plants transpire more in bright light as stomata open wider to facilitate photosynthesis. This is akin to how we seek shade on a scorching day.
Why is Understanding Water Transport Important?
Knowing how water moves through plants is not just a matter of botanical curiosity. It has practical implications, particularly in agriculture. Understanding the factors affecting water transport can help farmers optimize irrigation techniques, ensuring healthy crop growth and maximizing yields.
Travel Tip: Embrace the Power of Observation
Just as understanding water transport in plants enhances our appreciation for nature’s ingenuity, observing our surroundings while traveling can lead to fascinating discoveries. Whether it’s the intricate architecture of a historical landmark or the vibrant colors of a local market, taking the time to notice the details enriches our travel experiences.
 Plant Roots Absorbing Water
Plant Roots Absorbing Water
FAQs about Water Transport in Plants
Q: What happens to the water that reaches the leaves?
A: Most of the water that reaches the leaves is lost through transpiration, contributing to the water cycle. A small portion is used in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Q: Can plants absorb water through their leaves?
A: While the primary route of water absorption is through the roots, some plants can absorb a small amount of water through their leaves.
Q: How do plants in dry climates survive?
A: Plants in arid regions have developed various adaptations to conserve water, such as smaller leaves, deeper roots, and specialized photosynthetic pathways.
Travel Deeper into the World of Plants
Just as exploring a new city reveals hidden gems, delving deeper into the world of plants unveils fascinating insights. If you’re interested in learning more about plant life, consider visiting a botanical garden like the Singapore Botanic Gardens or the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, in London. These gardens offer a glimpse into the diversity of the plant kingdom and the crucial role plants play in our ecosystem.
At travelcar.edu.vn, we believe that understanding the world around us enhances our travel experiences. We encourage you to approach your next journey with a sense of curiosity and wonder, discovering the intricate connections that bind us to nature.