Have you ever wondered how quickly your brain processes information? Like a lightning-fast traveler navigating a complex network of roads, messages zip through your nervous system at incredible speeds. But just How Fast Do Messages Travel In Neurons? Let’s embark on a journey to understand the fascinating world of neuronal communication and uncover the speed at which our thoughts take flight.
The Need for Speed: Understanding Neuronal Communication
Imagine you’re strolling through the bustling streets of Tokyo, and suddenly, a car honks its horn. Your brain processes this information in a flash, allowing you to react quickly. This near-instantaneous response is possible due to the rapid-fire communication between neurons in your brain and nervous system.
But how does this communication actually happen?
The Neuron: A Cellular Highway
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit information throughout your body. They have three main parts:
- Dendrites: These branching structures receive signals from other neurons. Think of them as the “input” areas of the neuron.
- Cell body (Soma): This central part of the neuron processes incoming signals and decides whether to send a signal onward.
- Axon: This long, cable-like structure transmits signals away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands. It’s the “output” pathway of the neuron.
The Electrical and Chemical Relay Race
Neuronal communication is both an electrical and chemical process. It involves two key players:
- Action potential: This is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon of a neuron, much like a tiny electrical current.
- Neurotransmitters: These are chemical messengers that are released at the end of an axon (at a structure called the synapse) and bind to receptors on the dendrites of the next neuron, triggering a new action potential.
This intricate interplay of electrical and chemical signals allows messages to be relayed across the vast network of neurons in your body.
So, How Fast Do Messages Travel?
The speed at which a message travels in a neuron depends on several factors:
- Diameter of the axon: Thicker axons conduct signals faster, much like a wider pipe allows for faster water flow.
- Myelination: Some axons are covered in a fatty substance called myelin, which acts as insulation and speeds up signal transmission. Think of it as adding an express lane to a highway.
On average, messages can travel in neurons at speeds ranging from 1 to 120 meters per second (or roughly 2 to 270 miles per hour). That’s incredibly fast!
To put it in perspective, imagine you’re sending a message from the bustling Grand Bazaar in Istanbul to the serene gardens of the Taj Mahal in Agra. A neuronal signal could make that journey in a matter of milliseconds!
Factors Affecting Neuronal Speed and Travel Time
Just like road conditions can affect travel times, several factors can influence the speed of neuronal communication:
- Age: As we age, our neurons may lose some of their myelin, leading to slower signal transmission.
- Health conditions: Certain neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, can damage myelin and impair nerve conduction.
- Substance use: Drugs and alcohol can interfere with neurotransmitter function, affecting the speed and accuracy of neuronal communication.
The Importance of Speedy Signaling
The rapid transmission of messages in neurons is essential for:
- Sensory perception: Allowing us to quickly detect and respond to stimuli in our environment.
- Motor control: Enabling coordinated movements and reactions.
- Cognitive function: Underpinning our ability to think, learn, and remember.
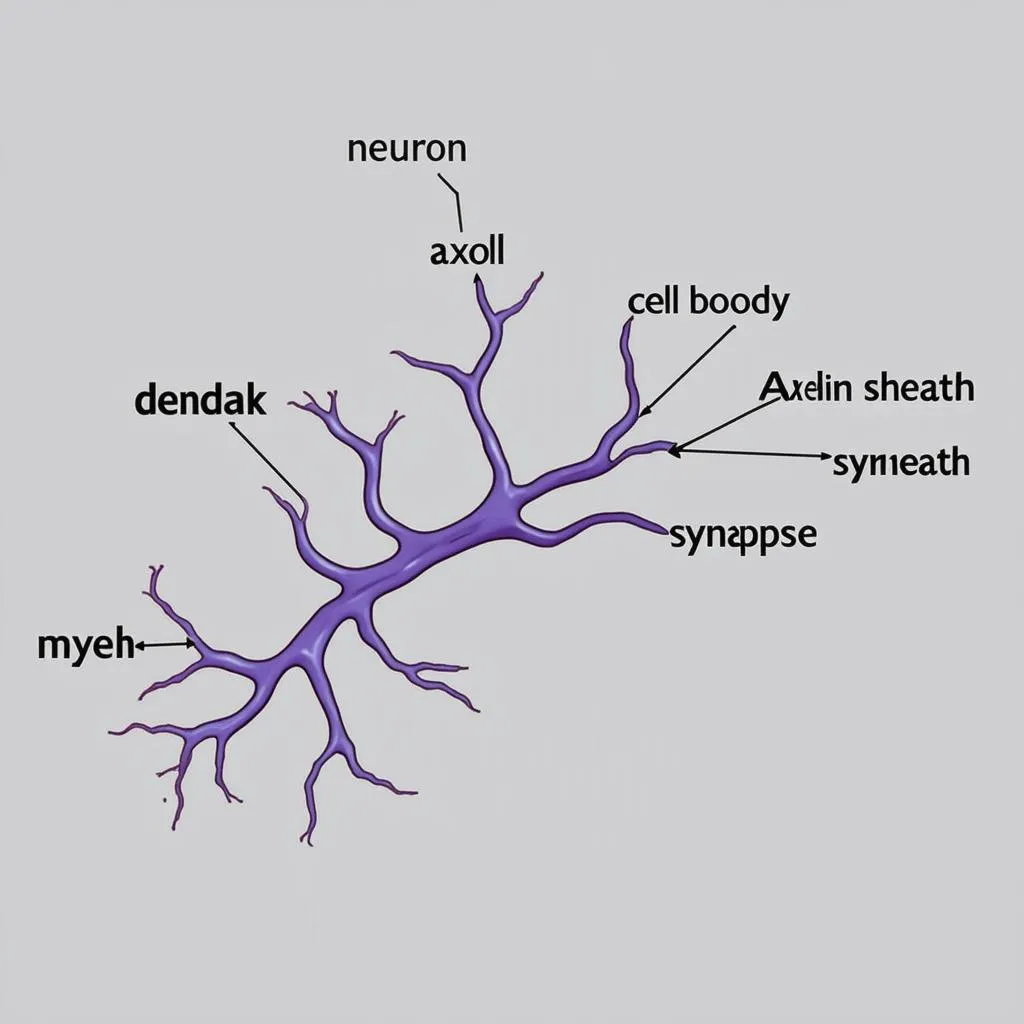 Structure of a Neuron
Structure of a Neuron
FAQs About Neuronal Communication
Q: Do all neurons transmit signals at the same speed?
A: No, the speed varies depending on factors like axon diameter and myelination.
Q: What happens if neuronal communication is disrupted?
A: Disruptions in neuronal communication can lead to a wide range of neurological and psychological disorders.
Q: Can we improve the speed of our neuronal communication?
A: While we can’t directly control the speed of individual neurons, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and mental stimulation can support overall brain health and function.
Travelcar.edu.vn: Your Guide to Exploring the World and Your Inner Universe
Just as we marvel at the interconnectedness of cultures and landscapes across the globe, understanding the intricate workings of our own nervous system reveals the wonder of our inner universe.
At Travelcar.edu.vn, we’re passionate about exploring the world around us and the fascinating processes that make life possible. From the bustling streets of Hanoi to the serene temples of Angkor Wat, we believe that every journey is an opportunity for discovery and growth.
 Neuronal Network
Neuronal Network
Conclusion
The speed at which messages travel in neurons is a testament to the remarkable efficiency of our nervous system. This intricate network allows us to perceive, act, and think with incredible speed and precision. So, the next time you catch a ball, solve a puzzle, or simply appreciate the beauty of a sunset, remember the lightning-fast communication happening within your own brain, a journey more awe-inspiring than any travel destination.
Let us know in the comments below what fascinates you most about the brain and how it shapes our experience of the world! And for more insightful articles on a variety of topics, be sure to explore the wealth of information available on Travelcar.edu.vn.