Have you ever gazed up at a silver bird soaring across the azure canvas of the sky and wondered, “Just how fast is that thing going?” The speed of air travel is a fascinating subject, and it’s not always as straightforward as it seems. Buckle up as we embark on a journey to explore the factors that influence how fast airplanes fly.
The Need for Speed: Factors Affecting Airplane Velocity
Several elements play a role in determining an airplane’s speed. Here are some of the most significant:
1. Aircraft Type
Just like cars, different airplanes are designed for different purposes and have varying capabilities. A nimble Cessna 172, often used for flight training, might cruise at around 120 mph, while a colossal Boeing 747 can reach speeds upwards of 550 mph.
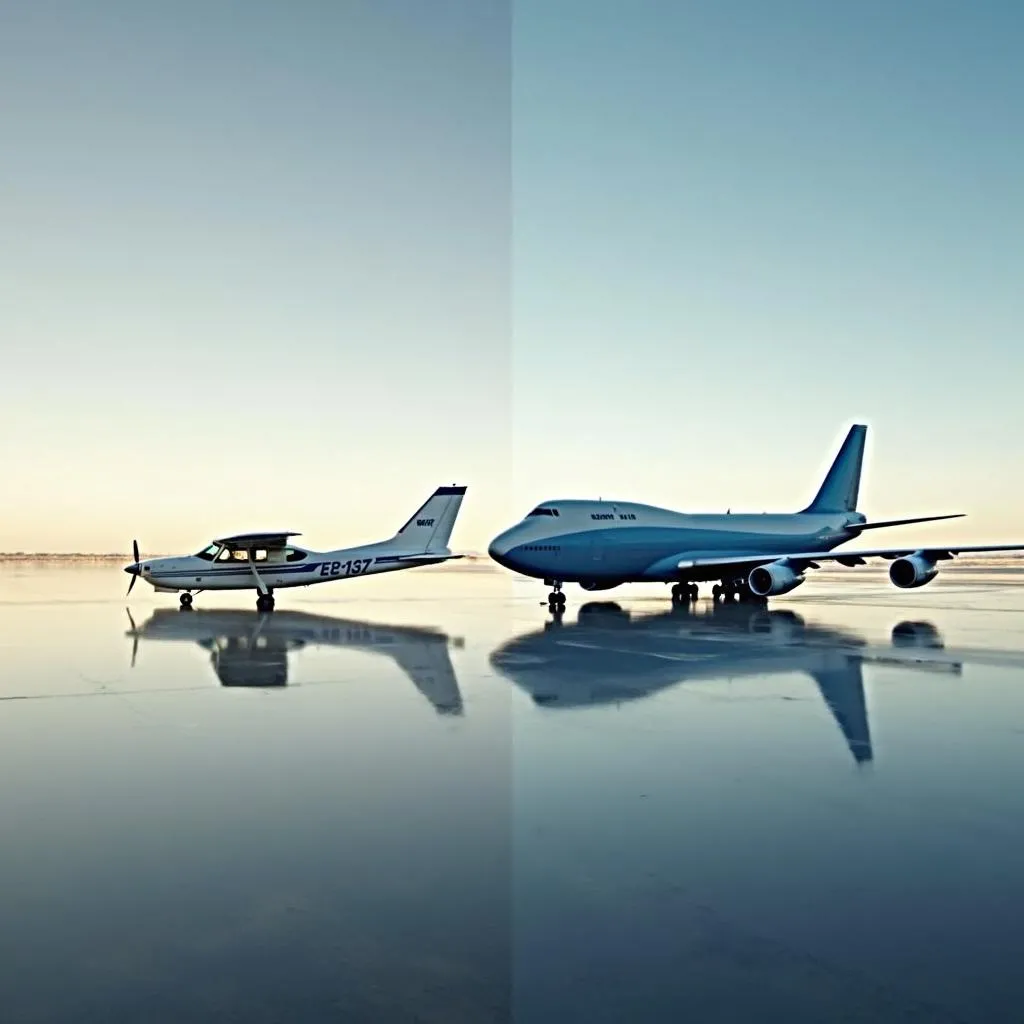 Different Types of Airplanes
Different Types of Airplanes
2. Altitude and Air Density
As an airplane ascends, the air gets thinner. This lower air density reduces drag, allowing the plane to fly faster. This is why commercial flights often cruise at altitudes around 35,000 feet.
3. Wind Conditions
Imagine trying to swim upstream against a strong current. Headwinds act similarly on airplanes, decreasing their ground speed. Conversely, tailwinds provide a helpful boost, increasing their speed relative to the ground.
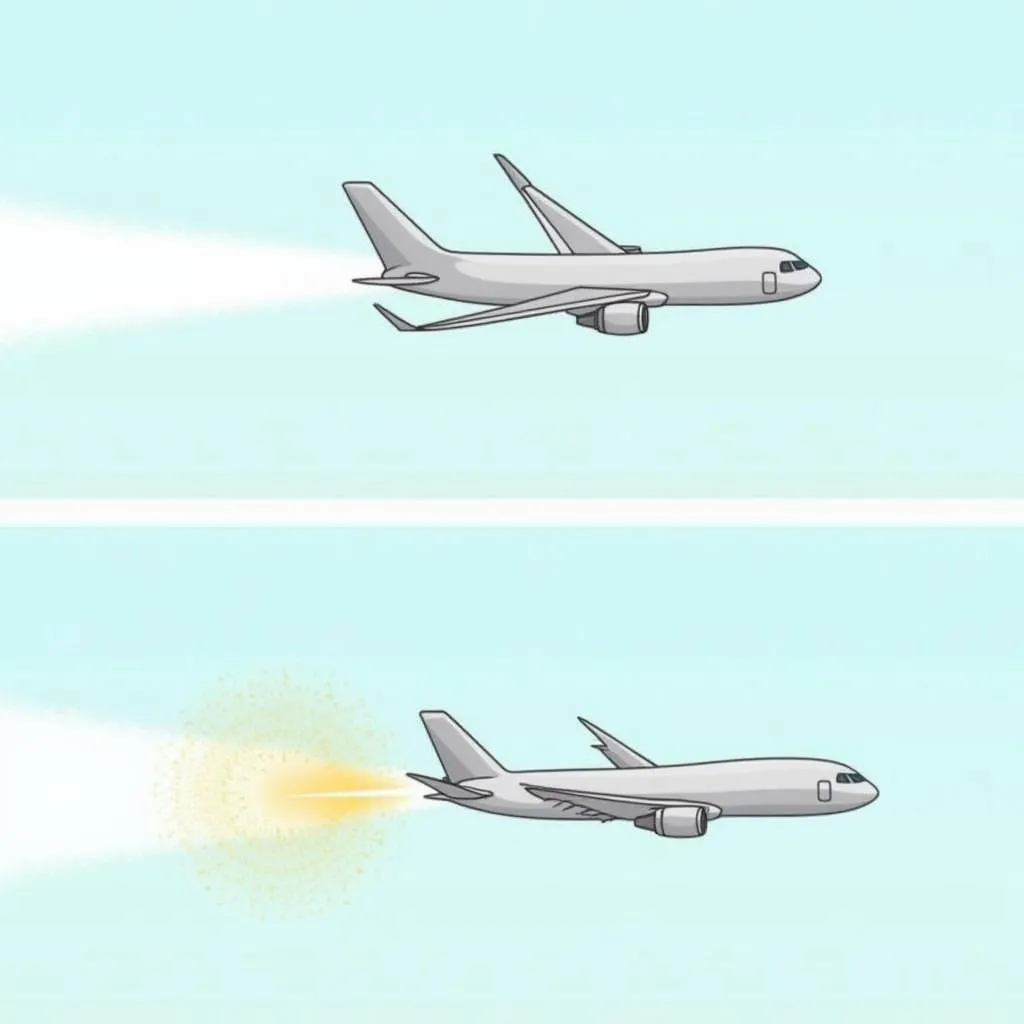 Airplane Flying in Different Wind Conditions
Airplane Flying in Different Wind Conditions
4. Weight and Load
A heavily loaded plane will naturally require more power to achieve and maintain its speed. This is why airlines carefully calculate weight distribution and fuel requirements for every flight.
The Sound Barrier and Beyond: Mach Speed
When discussing the speed of very fast aircraft, we often use Mach number. This unit measures the plane’s speed relative to the speed of sound.
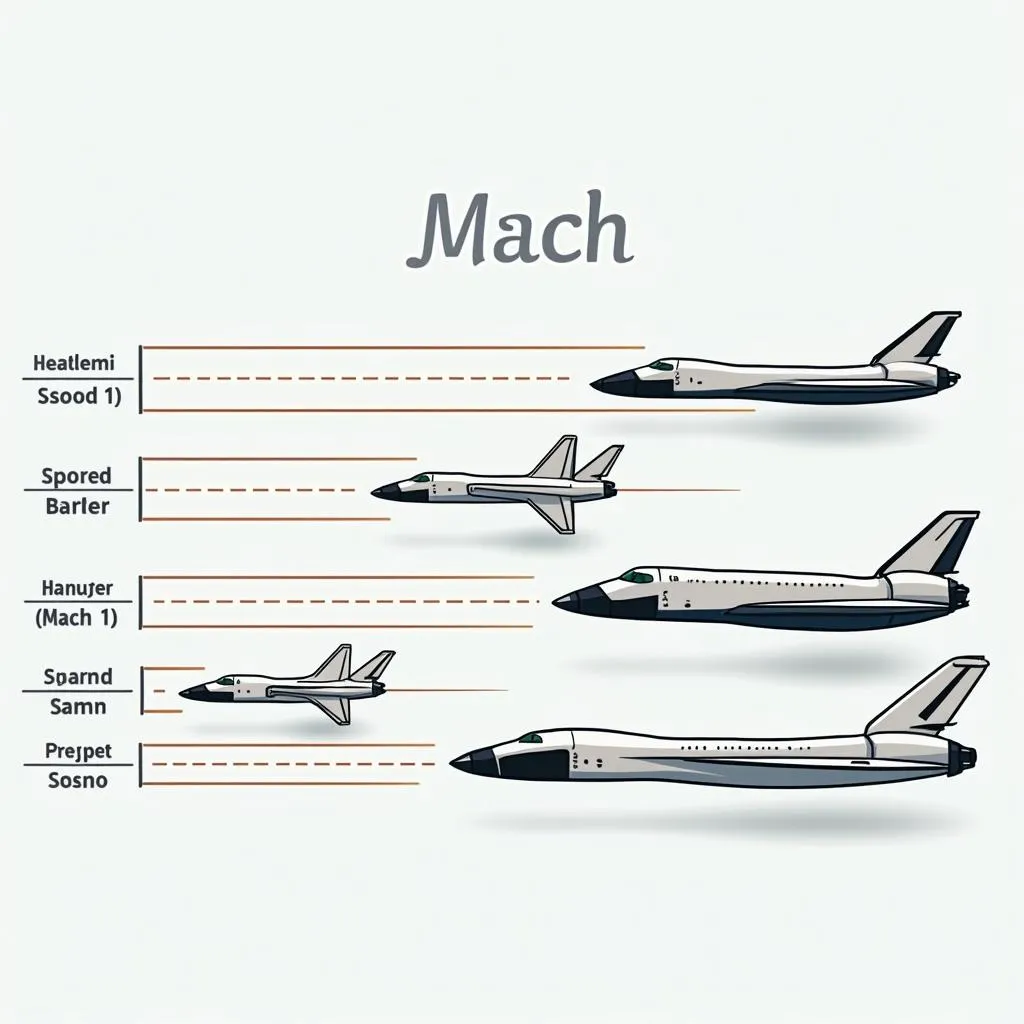 Visualization of Mach Speed Levels
Visualization of Mach Speed Levels
- Mach 1: The speed of sound, approximately 767 mph at sea level.
- Supersonic: Faster than Mach 1. Think of Concorde, the iconic supersonic passenger jet that could cross the Atlantic in under 4 hours.
- Hypersonic: Significantly faster than the speed of sound, typically Mach 5 and above. These speeds are the realm of experimental aircraft and space shuttles.

