Imagine this: you’re cruising down the Pacific Coast Highway, the California sun warming your face. You feel free, unburdened… but are you actually standing still? The answer, like many things in astronomy, is a bit more complicated than it seems. You see, the sun, that giant ball of fire in our sky, is constantly on the move. But just How Fast Is The Sun Traveling? Buckle up, space cadets, because we’re about to embark on a journey to uncover the speed of our celestial traveler.
The Cosmic Merry-Go-Round: The Sun’s Galactic Journey
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of the sun’s speed, we need to understand its place in the cosmic dance. Our sun, you see, isn’t just casually strolling through space. It’s actually caught in a cosmic whirlpool, orbiting the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
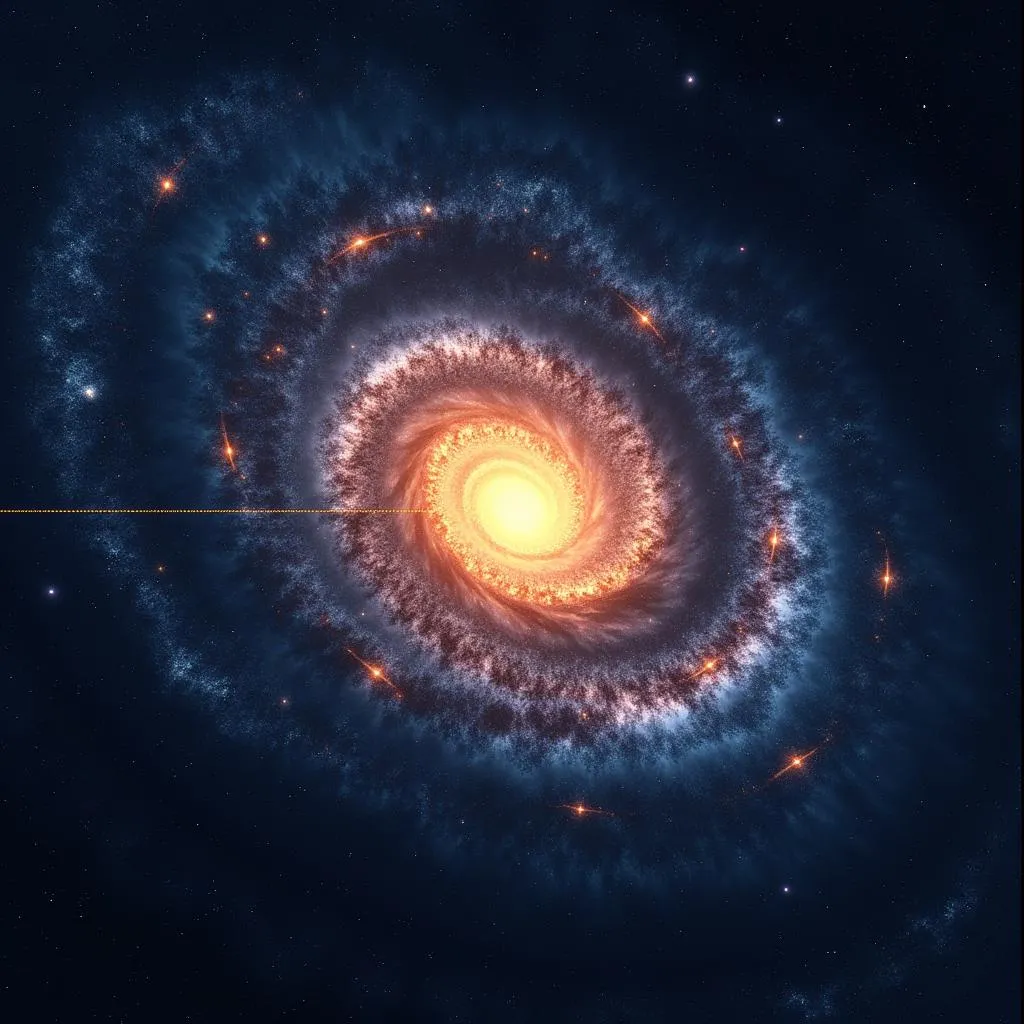 Milky Way Galaxy with Sun's Orbit
Milky Way Galaxy with Sun's Orbit
Imagine a gigantic merry-go-round with billions of riders, each rider a star like our sun. Now, imagine this merry-go-round spinning at a dizzying pace. That’s the Milky Way! Our sun, along with its planetary entourage (that includes us!), is whizzing around the galactic center at a mind-boggling speed of approximately 483,000 miles per hour (792,000 kilometers per hour)!
To put that into perspective, that’s like traveling around the entire Earth at the equator in less than three minutes! Talk about a fast-paced cosmic road trip!
Factors Influencing the Sun’s Speed
You might be wondering, why does the sun move at such a breakneck speed? Well, the answer lies in the complex interplay of gravity, mass, and distance.
The Milky Way, like all galaxies, is held together by gravity. The more massive an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. At the heart of the Milky Way lies a supermassive black hole, a cosmic monster with a gravitational pull so strong that it keeps billions of stars, including our sun, locked in orbit.
The distance between the sun and the galactic center also plays a role. As described by Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion, objects closer to the center of gravity move faster than those farther away. The sun’s position within the Milky Way, roughly two-thirds of the way out from the center, contributes to its impressive velocity.
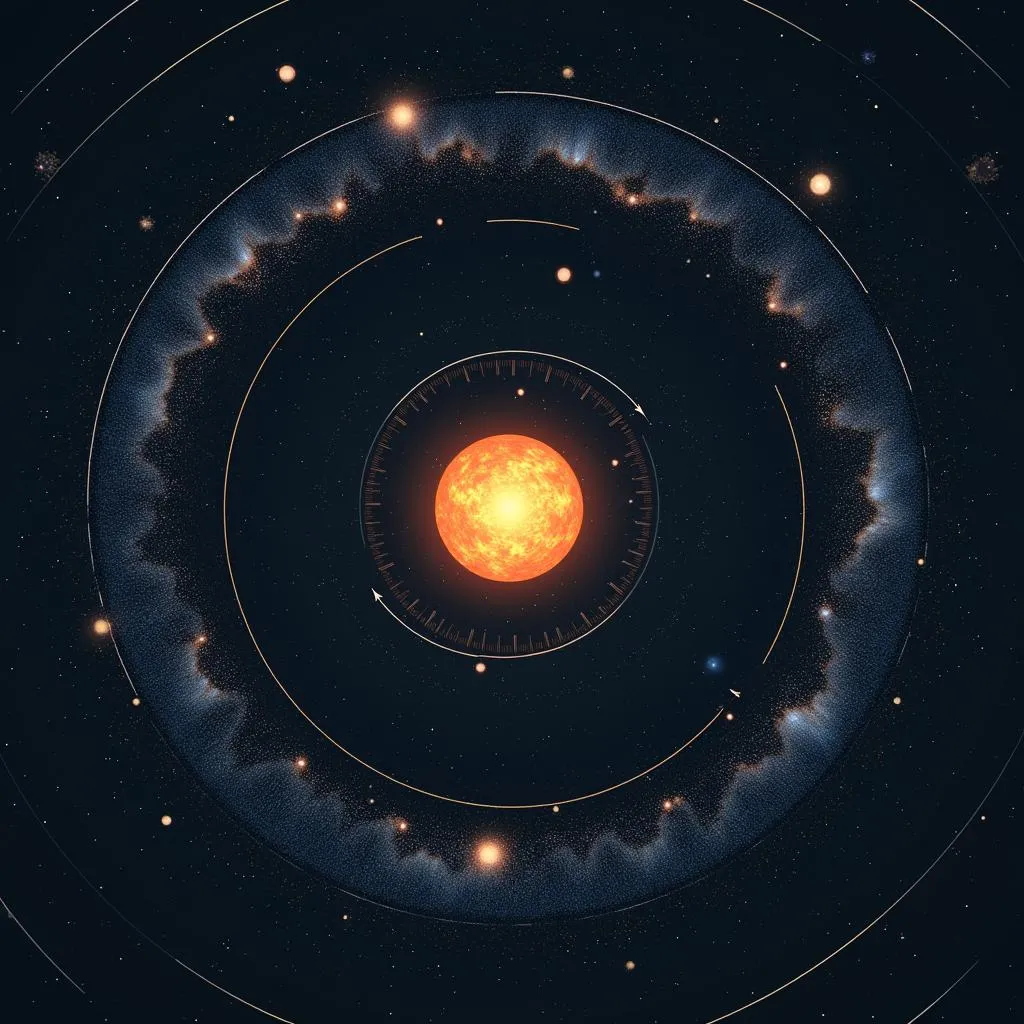 Sun's Orbit and Galactic Center
Sun's Orbit and Galactic Center
A Traveler in Time and Space
The sun’s incredible speed has profound implications for our understanding of time and space. It takes approximately 230 million years for the sun to complete one full orbit around the galactic center. That means the last time our solar system was in this part of the Milky Way, dinosaurs were just beginning to roam the Earth!
Our Cosmic Address: Pinpointing the Sun’s Location
Understanding the sun’s motion helps us pinpoint our cosmic address. We exist within the Orion Arm of the Milky Way, a relatively quiet and peaceful neighborhood compared to the bustling galactic center.
If you ever find yourself stargazing on a clear night, look towards the constellation Sagittarius. That’s the direction of the galactic center, the point around which our sun and billions of other stars are perpetually swirling.
 Night Sky with Sagittarius Constellation
Night Sky with Sagittarius Constellation
The Sun’s Movement: A Source of Wonder
The sun’s relentless journey around the Milky Way is a testament to the awe-inspiring scale and dynamism of the universe. It reminds us that we are part of something much grander than ourselves, constantly in motion, and forever bound to the rhythms of the cosmos.
So, the next time you’re gazing up at the sun, remember that it’s not just a stationary ball of light. It’s a celestial traveler, hurtling through space at unimaginable speeds, carrying us all along for the ride.

